- Share.Market
- 11 min read
- 27 Oct 2025
Imagine you could invest in the very pantry of the Indian middle-class household, the spice cabinet, the morning breakfast mix, and the ready-to-eat dinner solution.
That is precisely the opportunity being presented by the highly anticipated Orkla India IPO.
In a country where the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) market is not just growing but evolving at the pace of an express train, the listing of Orkla India, the powerhouse behind iconic, heritage brands like MTR Foods and Eastern Condiments, is set to be a landmark moment for the public market.
As investors scramble to assess the full potential of this FMCG giant, key questions arise: What are the fundamental Orkla India IPO details, from the price band to the timeline? How strong is the company’s growth outlook as it attempts to replicate its regional success nationwide?
And most critically, what are the inherent risks of investing in a pure OFS structure within a highly competitive consumer staples sector?
Before you decide whether to add this flavour-rich stock to your investment portfolio, let’s delve into a comprehensive analysis of this.
That is a great question! Let’s talk about the overall economic backdrop and the performance of the packaged food industry in India, drawing on the recent market analysis available in the sources.
The Packaged Food Industry Performance
The packaged food market in India is highly dynamic and growing rapidly, benefiting immensely from the macro trends such as urbanization, changing lifestyles, and rising female workforce participation.
Here’s a Snapshot of the Market performance:
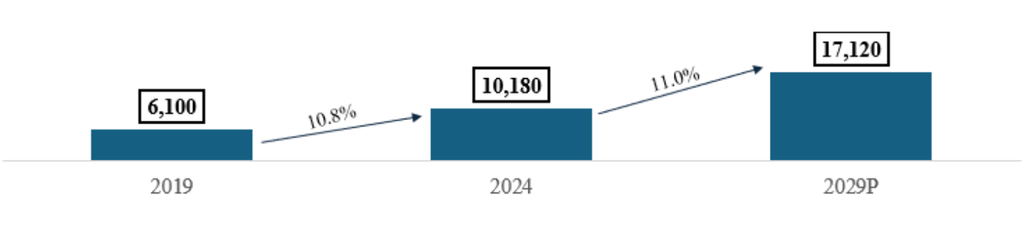
- Overall Market Growth: The Indian packaged food market was valued at ₹10,180 billion in Fiscal 2024. It has shown a strong CAGR of 10.8% since Fiscal 2019 and is projected to expand significantly to ₹17,120 billion by Fiscal 2029, reflecting an expected CAGR of 11.0%.
Indian Packaged Food Market (in INR billion) (Fiscal); CAGR (%)
- Segment Growth: The market’s high growth is fueled by a massive shift towards branded, standardized products, moving away from loose or unbranded alternatives.
The industry is strongly influenced by two key product categories: Spices and Convenience Foods.
1. Spices Market
India holds a dominant position globally in spices, being the world’s largest producer, consumer, and exporter.
- Market Size: The overall Indian spices market (including both packaged and loose spices) reached ₹1,230 billion in Fiscal 2024.
Indian Spices Market – By Value (in ₹ billion) (Fiscal) ; CAGR
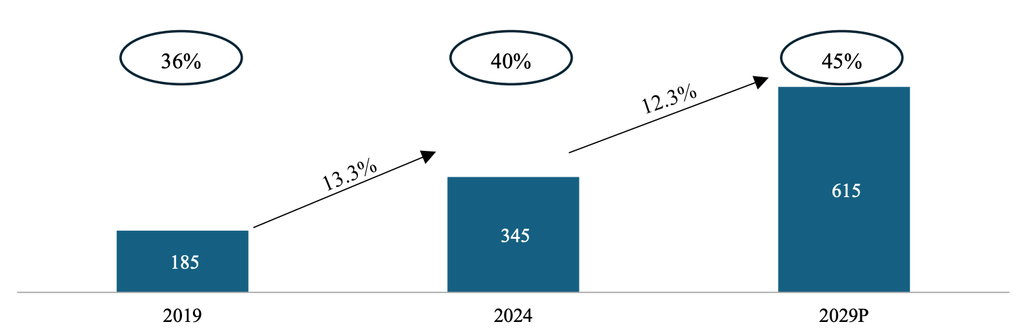
- Packaged Growth: Crucially, the packaged spices market is growing faster than the overall market, estimated at ₹345 billion in Fiscal 2024. This segment grew at a CAGR of approximately 13.3% since Fiscal 2019. This growth is projected to continue, reaching ₹615 billion by Fiscal 2029.
Indian Domestic Packaged Spices Market- By Value (in ₹ billion)
- Key Drivers: Consumers are increasingly choosing packaged spices due to rising awareness of food safety and hygiene, which addresses concerns about contamination or adulteration often associated with loose spices. The growing preference for pre-mixed or blended spices also drives this segment, offering easy-to-use solutions with consistent taste.
2. Convenience Food Market
The convenience food market includes categories like Ready-to-Cook (RTC) and Ready-to-Eat (RTE) foods.
- Market Size and Potential: This market is currently valued at ₹79 billion as of Fiscal 2024 but is considered to be at a nascent stage compared to developed economies like the US and China.
Market Size of Convenience Food Industry in India (Fiscal)
- High Growth Rate: Driven by busy, evolving lifestyles, the convenience food market is projected to reach ₹166 billion by Fiscal 2029, indicating a strong projected CAGR of 16%.
- Changing Consumption Patterns: Increasing female workforce participation and diminishing culinary skills among younger generations are driving demand for quick, authentic, and nutritious meal solutions.
Retail Transformation
The way these packaged goods are bought is also changing significantly.
- Traditional Dominance: General Trade (traditional neighborhood stores, or kirana shops) remains the main sales channel, accounting for approximately 76% of packaged food sales in Fiscal 2024.
- Emerging Channels: Modern Trade (supermarkets and organized retail) and especially E-commerce/Quick-commerce are gaining traction fast. Quick-commerce, driven by digital adoption and the convenience of rapid delivery, is expected to capture 10.0% of the packaged food market by Fiscal 2029.
In short, the Indian economy is stable and growing, supported by strong demographic and consumption trends.
This environment is creating a robust, expanding market for packaged food companies, particularly those focused on convenience, quality, and adapting to localized tastes.
Orkla India: Company Overview
Orkla India Limited is a multi-category Indian food company with operations spanning several decades.
The company offers a diverse range of products designed to cater to every meal occasion, including breakfast, lunch, snacks, dinner, beverages, and desserts.
The company’s position in the market is strong, and as of Fiscal 2024, it was one of the top four companies in terms of revenue from operations among selected leading spices and convenience food peers.
The Brands: MTR and Eastern
Orkla India’s products are sold primarily under two major, well-established brands: MTR and Eastern.
Both brands are crafted with authenticity and tradition and are deeply rooted in the South Indian culinary heritage.
- MTR Brand: Originally established in 1924, MTR has been a key brand of the company since its incorporation in 1996. The brand ethos focuses on providing local, quality food products, specializing in vegetarian food. Orkla India formally acquired the exclusive rights to the MTR brand for processed packaged foods and beverages in 2007, as a pre-condition to the acquisition of the company by Orkla ASA.
- Eastern Brand: Founded in 1983, Eastern has spent over four decades expanding its portfolio of Spices and Convenience Foods. This brand focuses on local and quality food products, with a special emphasis on Kerala cuisine. Orkla India acquired Eastern Condiments in March 2021, and it was subsequently amalgamated into Orkla India in September 2023.
These brands are considered household names, particularly in the core markets of Karnataka and Kerala, where they enjoy strong consumer loyalty and trust.
In fact, the MTR and Eastern brands are the most widely distributed brands in Karnataka and Kerala for spices.
Core Product Portfolio
Orkla India’s business is mainly focused on two key product categories: Spices and Convenience Foods.
As of June 30, 2025, the company’s portfolio included approximately 400 products across these categories, selling about 2.3 million units on average every day.
The contribution of these categories to revenue from product sales is consistently high:
| Product Category | For the three months ended June 30, 2025 | Fiscal 2025 |
| Spices | 66.3% (₹3,899.1 million) | 66.6% (₹15,712.5 million) |
| Convenience Foods | 33.7% (₹1,981.8 million) | 33.4% (₹7,870.7 million) |
- Spices: This category includes blended spices (like Sambar, Chicken, and Rasam Masala) and pure spices (such as Chilli, Turmeric, Coriander, and Cumin). The company holds a market leader position in packaged spices in Karnataka (31.2% share) and is the largest player in Kerala.
- Convenience Foods: This category simplifies cooking through products like:
- Ready-to-Cook (RTC) foods: Dry mixes (like Gulab Jamun mix or Rava Idli mix) and wet batters (like idli dosa batter).
- Ready-to-Eat (RTE) foods: Fully cooked, packaged items like Paneer Butter Masala, Dal Makhani, and various rice dishes.
- Vermicelli and other products like beverages, pickles, and cooking aids.
Global Parentage and Corporate Structure
Orkla India is a subsidiary of Orkla ASA, a Norway-listed industrial, long-term investment company focused on brands and consumer-oriented companies.
- Promoters: The company’s promoters are Orkla ASA, Orkla Asia Holding AS, and Orkla Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd..
- Benefits of Parentage: Being part of the Orkla Group has helped Orkla India enhance its corporate governance, operational standards, food safety and quality practices, risk management, and information technology.
Distribution and Market Reach
The company relies on an extensive and diverse distribution network, enabling deep penetration, especially in South India.
- Domestic Network: As of June 30, 2025, the network included 834 distributors and 1,888 sub-distributors across 28 states and six union territories in India.
- Channel Presence: The company partners with 42 modern trade retail chains and six e-commerce and quick commerce channels. General Trade (GT) still dominates, contributing 77.1% of total domestic sales for the three months ended June 30, 2025, while E-commerce and Quick Commerce channels saw strong growth, reaching 8.6% of domestic sales in the same period.
- Geographic Focus: Sales are concentrated in South India, which contributed 70.0% of the revenue from sale of products in the three months ended June 30, 2025.
- International Reach: Exports are a key part of the business, catering to the Indian diaspora globally. As of June 30, 2025, Orkla India exported its products to 45 countries. Revenue from international customers accounted for 20.4% of sale of products in the three months ended June 30, 2025.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Orkla India uses an efficient manufacturing model that balances owned facilities with contract manufacturing to be capital-efficient and meet growing demand.
- Owned Facilities: As of June 30, 2025, the company operated nine owned manufacturing facilities in India, primarily located in South India (eight of the nine are in the South, specifically Karnataka, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh). These units have a total installed capacity of 182,270 TPA.
- Contract Manufacturing: The company partners with 18 contract manufacturers in India (15 of which are in South India) and three outside India (in UAE, Thailand, and Malaysia). This model helps enhance cost efficiency and agility.
Orkla India IPO: Key Details and Structure
Tapping India’s packaged food boom, Orkla’s IPO allows investors to taste a piece of MTR and Eastern’s growth story.
| IPO Date | October 29, 2025 to October 31, 2025 |
| Sale Type | Offer For Sale |
| Issue Price Band | ₹695 to ₹730 per share |
| Face Value | ₹1 per share |
| Minimum Lot Size | 20 Shares |
| Minimum Investment | ₹13,900 |
| Total Issue Size | ₹1,667.54 Cr |
Where Will the Funds Be Used?
The most important detail regarding the use of funds is that Orkla India Limited will not receive any proceeds from the Offer.
To achieve the benefits of listing the Equity Shares on the Stock Exchanges, which is expected to enhance the Company’s visibility and brand image and provide liquidity and a public market for the shares in India.
In summary, this IPO is primarily about the existing investors monetizing a portion of their stake, not about raising fresh capital for the company’s business operations
Orkla India Financial Performance
Behind the beloved brands, the financial ingredients reveal a story of consistency and efficiency. So let’s unpack the core metrics:
| Particulars (₹ million) | Fiscal 2023 (FY23) | Fiscal 2024 (FY24) | Fiscal 2025 (FY25) | Q1 FY26 |
| Revenue from Operations | 21,724.8 | 23,560.1 | 23,947.1 | 5,970.0 |
| Adjusted EBITDA | 3,124.4 | 3,436.1 | 3,964.4 | 1,117.5 |
| Adjusted EBITDA Margin (%) | 14.4% | 14.6% | 16.6% | 18.7% |
| PAT | 3,391.3 | 2,263.3 | 2,556.9 | 789.2 |
| PAT Margin (%) | 15.6% | 9.6% | 10.7% | 13.2% |
The core trend reveals strong underlying operational efficiency marked by a steady improvement in adjusted EBITDA margins since Fiscal 2023, accelerating significantly into the most recent quarter.
The major factor driving profitability has been the deflationary environment, specifically the sharp decrease in raw material and packaging costs.
By effectively managing these lower input prices and prioritizing volume growth over immediate price increases, the company successfully expanded its profit margins and captured greater market share.
However, the reported Profit After Tax figures for Fiscal 2023 appear disproportionately high due to a non-recurring tax credit related to a key merger, which makes direct year-on-year comparisons of the net profit misleading.
The true financial narrative is one of strengthening efficiency and robust cost control.
Key Strength of Orkla India
- Market Leader in South India: Leading brands (MTR and Eastern) have built significant market share in packaged spices in South India, leveraging deep local taste understanding and strong consumer loyalty.
- Focus on Product Innovation: A multi-category food company focusing on innovation by adapting recipes and formats. It pioneered products like Rava Idli and the 3-Minute range, meeting modern consumer needs.
- Extensive Global Distribution: An extensive network includes 834 distributors domestically and exports to 45 countries. Strong presence spans general trade, modern trade, and growing e-commerce/quick commerce channels.
- Efficient Manufacturing Model: Balances nine owned facilities with contract manufacturing for flexibility and cost efficiency. Manufacturing includes automation and holds stringent BRCGS and ISO 22000 quality certifications.
- Strong Global Parentage: Supported by Norway-listed Orkla ASA, providing enhanced governance, operational standards, food safety expertise, and continuous access to global centers of excellence.
Key Risks of Orkla India
- Raw Material Price Volatility: Costs depend on volatile commodity prices (chilli, turmeric, cumin) influenced by climate and global supply. Inability to manage or pass on price increases could negatively affect margins and results.
- Product Contamination Risk: Improper processing, storage, or real/perceived contamination risks can lead to regulatory action, product recalls, damage to brand reputation, and significant legal liabilities.
- Reliance on Key Suppliers: The company is dependent on raw material suppliers; the top ten contributed 37.9% of total purchases in Q1 FY26. Loss of these suppliers or delivery delays could severely disrupt operations.
- South India Concentration: 70.0% of revenue is derived from South India, where most owned and contract manufacturing is located. Unfavorable regional events could cause adverse operational disruptions.
- FSS Act Regulatory Actions: The company is party to 126 pending statutory or regulatory actions, mainly under the FSS Act, regarding alleged contamination, misbranding, or substandard products. Adverse results hurt reputation.
Conclusion
The Orkla India IPO presents a compelling opportunity to invest in a market leader with iconic brands (MTR and Eastern) deeply integrated into the Indian consumer pantry. The company’s financial narrative is one of strengthening operational efficiency, demonstrated by robust margin expansion driven by smart cost management and market share-focused volume growth.
However, prospective investors must be cautious. The offering is a pure Offer for Sale (OFS), meaning the company raises no fresh capital for its own growth. Furthermore, the reliance on raw material deflation for recent profit surges and intense competition in the FMCG sector represent inherent investment risks.
While the fundamentals are strong, but investment decision requires careful evaluation of these risk factors alongside the promising growth outlook.